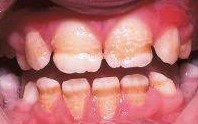
Understanding Enamel Hypoplasia
Enamel hypoplasia is a condition in which there is a deficiency in the development or formation of tooth enamel while the teeth are still developing in the jaw. It affects the appearance of the teeth and can lead to dental sensitivity, tooth decay, and other oral health concerns. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, types, prevention, line of treatment, reversal, and home remedies of enamel hypoplasia.
What Are The Causes of Enamel Hypoplasia?
Several factors can cause enamel hypoplasia, including:
1. Malnutrition: A diet lacking in essential nutrients, including vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus, can lead to enamel hypoplasia.
2. Genetic factors: Some genetic conditions can impact the development of tooth enamel.
3. Infections: Infections that occur during a child’s development can impact the development of tooth enamel.
4. Trauma: Injuries to the teeth or jaws can impact the development of tooth enamel.
5. Exposure to toxins: Exposure to lead, mercury, or other toxins can affect the development of tooth enamel.
What Are The Symptoms of Enamel Hypoplasia?
The symptoms of enamel hypoplasia may vary depending on the severity of the condition and the location of the affected teeth. Some common symptoms may include:
1. Discoloration of the teeth, including white, yellow, or brown spots or pits.
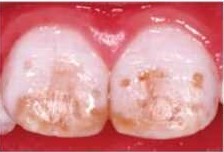
2. Teeth that are more sensitive to temperature and pressure.
3. Increased risk of cavities or decay.
4. Rough or pitted enamel surface.
What Are The Types of Enamel Hypoplasia?
Enamel hypoplasia is a condition in which the enamel layer of the teeth is deficient or damaged during the developmental stage. There are several types of enamel hypoplasia that can affect both primary and permanent teeth.
The most common types of enamel hypoplasia include:
1. Hereditary Enamel Hypoplasia:
Hereditary enamel hypoplasia is a genetic condition that affects the development of the enamel layer. It can cause white or yellowish-brown patches or pits on the teeth, and can also lead to increased sensitivity and vulnerability to cavities. This type of enamel hypoplasia is usually present from birth or develops shortly thereafter.
2. Developmental enamel hypoplasia:
Developmental enamel hypoplasia can occur due to a variety of factors during the developmental stage of the teeth. This can include maternal illness, malnutrition, exposure to toxins such as lead or chemotherapy drugs, and certain medical conditions such as celiac disease. This type of enamel hypoplasia can cause pits, grooves, or rough areas on the teeth, and can also result in increased cavities and sensitivity.
3. Trauma-Induced Enamel Hypoplasia:
Trauma-induced enamel hypoplasia can occur due to trauma to the teeth or jaw during the developmental stage. This can include injury from falls, accidents or abuse, or even tooth decay or dental procedures. Trauma-induced enamel hypoplasia can cause localized defects in the enamel layer that may appear as discoloration, pitting or smaller than the normal size of the tooth.
4. Environmental Enamel Hypoplasia:
Environmental enamel hypoplasia can occur due to environmental factors such as an injury or infection that disrupts the enamel development. Symptoms can include white or yellowish-brown defects in the tooth, pitting, or even altered shape or size of the tooth.
5. Acquired Enamel Hypoplasia:
Acquired enamel hypoplasia can occur in permanent teeth that have already developed and erupted. This can be caused by injury to the tooth, infections, exposure to toxins, and other environmental or medical factors. Acquired enamel hypoplasia usually causes white or brownish spots, grooves or pits on the tooth surface.
Prevention of Enamel Hypoplasia
Prevention of enamel hypoplasia is vital to maintain proper dental health. A few preventive steps include:
1. Eating a balanced and nutritious diet rich in vitamins and minerals essential for dental health.
2. Maintaining good oral hygiene habits by brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using mouthwash.
3. Avoiding exposure to toxins and harmful substances that may affect the development of tooth enamel.
4. Regular dental check-ups with your dentist to identify and treat any potential dental problems.
What Is The Line of Treatment for Enamel Hypoplasia?
Treatment for enamel hypoplasia depends on the extent and severity of the condition. Treatment is usually focused on addressing any dental problems caused by the condition, such as sensitivity, cavities, and cosmetic concerns like discoloration. Here are some possible treatment options:
1. Fluoride treatments:
Fluoride varnish or fluoride rinses can help remineralize the affected areas, making them less susceptible to decay.
2. Bonding:
In cases of mild enamel hypoplasia, bonding may be used to fill in areas of missing or damaged enamel. Bonding is a cosmetic procedure that involves adding a resin-based material to the affected teeth to restore their appearance.
3. Crowns or veneers:
In cases of severe enamel hypoplasia, where the damage is extensive, dental crowns or veneers may be used to correct the appearance and functionality of the tooth. These are custom-made restorations that are placed over the existing tooth, covering the damaged area.
4. Dental filling:
Dental fillings may be used for areas where there is limited damage or missing enamel. This material can help restore the shape and function of the tooth.
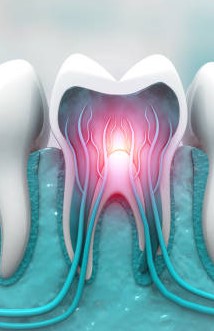
5. Root canal therapy:
In rare cases, where the damage to the tooth is extensive and has affected the pulp, root canal therapy may be necessary. This procedure involves the removal of the damaged pulp, filling in the space, and capping the tooth with a crown.
Prevention is also a key component of treating enamel hypoplasia. Maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding sugary and acidic foods, using a fluoride toothpaste, and visiting the dentist regularly can help prevent further damage and decay.
Enamel hypoplasia is a condition that can affect the appearance and function of your teeth, and it is essential to treat it promptly. A dental professional can guide you in selecting the best treatment method for your specific condition.
How To Reverse Enamel Hypoplasia?
Enamel hypoplasia cannot be reversed once the tooth enamel has formed, but treatment can help restore the appearance and strengthen the teeth. However, preventive measures such as a balanced diet, good oral hygiene habits, and avoiding exposure to toxins can prevent enamel hypoplasia from occurring.
Home Remedies for Enamel Hypoplasia
There are some home remedies that can help improve the appearance of your teeth, including:
1. Oil pulling: Swishing coconut oil or sesame oil in the mouth for 10-15 minutes can help improve the strength and appearance of tooth enamel.
2. Saltwater rinse: Gargling with warm saltwater can help reduce inflammation and maintain healthy oral hygiene.
3. Baking soda: Brushing your teeth with a paste of baking soda and water can help remove surface stains and improve the overall appearance of your teeth.
Conclusion
Enamel hypoplasia is a dental condition that can affect the appearance and health of your teeth. Maintaining good oral hygiene habits, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding exposure to toxins can prevent enamel hypoplasia from occurring. If you suspect enamel hypoplasia, it is essential to seek dental treatment promptly to identify and treat the condition before it leads to other dental problems. With proper dental care and attention, enamel hypoplasia can be effectively managed, and the health of your teeth can be maintained.