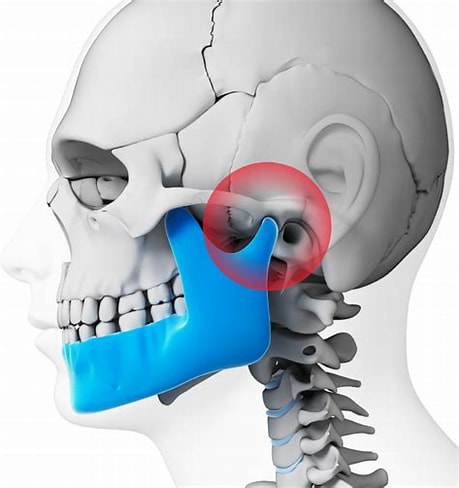
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is a hinge joint that connects the jawbone (mandible) to the skull at the temporal bone. This joint enables the jaw to move up and down and side to side, which is essential for talking, chewing, and yawning. However, when the TMJ is damaged or not functioning correctly, it can cause various disorders, collectively known as temporomandibular joint disorders or TMD.
Page Contents
ToggleCauses of TMJ Disorders
The precise cause of TMJ disorders is not yet known, but there are several factors that may lead to TMJ problems. These include:
1. Trauma or Injury – any significant injury to the jaw or jawbone, such as a tumble, car accident or a punch to the face can cause TMJ-related problems.
2. Arthritis – different types of arthritis like rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and psoriatic arthritis can cause TMJ problems.
3. Stress – Clenching of the jaw caused by stress can lead to pain and dysfunction, while anxiety or depression may make the pain more severe.
4. Teeth Grinding and Jaw Clenching – Also referred to as bruxism, teeth grinding, and jaw clenching can damage the TMJ over time.
5. Malocclusion (improper bite) – when teeth are misaligned or if they don’t fit together correctly, it can also strain the TMJ and lead to TMD.
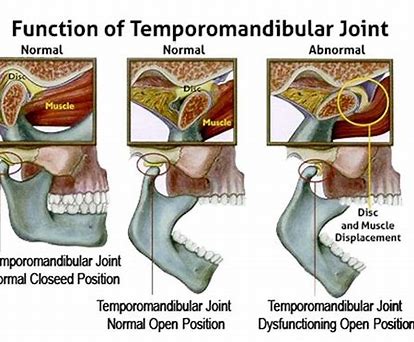
Common TMJ Disorders
1. Myofascial Pain Disorder – This disorder causes pain and discomfort in the muscles that control jaw movement. It often results from stress or overusing the TMJ muscles.
2. Internal Derangement – Internal derangement happens when the disc located between the jaws and skull is damaged or displaced from its original position. This can cause clicking or popping sounds when opening or closing the mouth.
3. Arthritis – Arthritis is an inflammatory condition that can affect the TMJ and lead to pain and difficulty when moving the jaw.
4. TMJ Ankylosis – is a rare condition in which the TMJ joint becomes fused, making it nearly impossible to move.
5. Jaw dislocation– Jaw dislocation can result from trauma or injury, and it can cause pain, difficulty speaking, and trouble chewing.
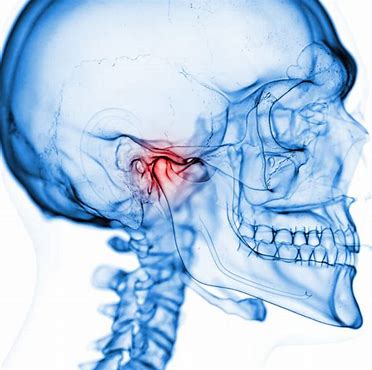
Symptoms of TMJ Disorders
The most common symptoms of TMJ disorders include jaw pain, difficulty chewing, aching facial pain, and stiffness in the jaw. Other signs include ear pain, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), dizziness, headaches, and difficulty opening or closing the mouth.
The symptoms of TMJ (temporomandibular joint) disorders can vary from person to person and depend on the severity of the condition. Here are some common symptoms of TMJ disorders:
1. Pain: Pain is the most common symptom of TMJ disorder and can be felt in the jaw, face, ear, or neck. Pain intensity may vary and can be sharp, dull, or aching.
2. Difficulty with jaw movement: TMJ disorders can cause difficulty in opening and closing the mouth, and limited side-to-side or forward motion of the jaw.
3. Clicking or popping sounds: You may hear a clicking or popping sound when you open or close your mouth. This sound could be due to the movement of the jawbone and cartilage when the joint is not properly aligned.
4. Locking of the jaw: In some cases, the jaw might lock in an open or closed position.
5. Tinnitus: TMJ disorders may cause ringing or buzzing in the ear, called tinnitus.
6. Headaches: You may experience tension-type headaches or migraine-like headaches due to TMJ disorders.
7. Ear pain: TMJ disorders can refer pain to the ear causing pain or discomfort.
It is important to note that some TMJ disorders may not cause any symptoms and may not need any treatment. However, if you experience any of the above symptoms, consult your dentist for proper evaluation and treatment.
Treatment options for TMJ disorders
The treatment for TMJ-related issues typically depends on the cause of the disorder. Some treatment options include:
1. Over-the-counter pain relievers – These can help alleviate the pain associated with TMJ disorders.
2. Prescription medications – In some cases, prescription medications may be necessary to ease the pain and reduce inflammation.
3. Physiotherapy and exercises – Specific TMJ exercises and stretches may help relax muscles that control jaw function.
4. Bite splints and Mouthguards – These dental devices can correct misaligned jaws, preventing teeth grinding or clenching.
5. Surgery – If other treatments are unsuccessful or if there is severe damage to the TMJ joint, surgery may be required to repair or replace the deteriorated components.
Conclusion
TMJ disorders can vary considerably in symptoms, severity, and treatments. Understanding the causes behind the disorder is essential for developing an effective treatment plan. Therefore, it’s crucial for patients with TMJ-related disorders to seek professional help from trained health care providers for proper diagnosis and treatment. Proper Jaw care includes avoiding excessive jaw movement, eating softer foods, managing stress levels, and refraining from chewing gum.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about TMJ (temporomandibular joint) disorders:
1. What causes TMJ disorders?
The causes of TMJ disorders are not fully understood, but several factors can contribute to their development, including injury to the jaw joint, teeth clenching or grinding (bruxism), misaligned teeth or bite patterns, arthritis, and stress.
2. What are the symptoms of TMJ disorders?
The symptoms of TMJ disorders include pain or tenderness in the jaw, difficulty opening or closing the mouth, clicking or popping sounds when opening or closing the mouth, locking of the jaw, headaches or migraines, toothaches, neck pain, ear pain, and tinnitus (ringing in the ears).
3. How are TMJ disorders diagnosed?
TMJ disorders can be diagnosed through a physical examination of the jaw joint and surrounding muscles. Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans may be recommended to assess the condition of the joint.
4. What are the treatment options for TMJ disorders?
The treatment for TMJ disorders typically includes self-care measures, such as heat or ice therapy, gentle jaw exercises, and stress management techniques. Medications, dental procedures, physical therapy, and surgery may also be used to manage the condition, depending on severity.
5. Can TMJ disorders be prevented?
Preventing TMJ disorders involves taking care of your teeth and avoiding habits like teeth clenching or grinding. Maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding chewing on hard or sticky foods, and practicing relaxation techniques to reduce stress can also help prevent TMJ disorders.
6. Do I need to visit a dentist for TMJ disorders?
Yes, a dentist can evaluate your symptoms and develop a customized treatment plan to manage TMJ disorders. They may also refer you to a specialist, such as an oral surgeon, if surgical intervention is required.
If you experience any symptoms of TMJ disorders, consult your dentist or healthcare provider for proper evaluation and treatment.