Tongue bite refers to accidentally biting your tongue with your teeth while talking, eating, or performing any other activity involving your mouth. It can cause pain, discomfort, swelling, and in some cases, bleeding. Mild tongue bites usually heal on their own, while severe bites may require medical attention. To prevent tongue bites, it is advisable to eat slowly and avoid talking while eating.
The main reasons people bite their tongue is due to the accidental placement of their tongue between their teeth while speaking, chewing, or performing other mouth-related activities. This can cause them to unknowingly bite down on their tongue and cause injury. Additionally, being under stress, experiencing muscle spasms or twitches, or having a medical condition that affects the muscles and nerves in the mouth can also cause tongue biting. In some cases, certain medications or substances can cause involuntary movement of the tongue, leading to accidental biting.

CAUSES OF TONGUE BITE?
There are several causes of tongue bite that can occur frequently, including:
1. Malocclusion: When the teeth do not align properly, biting the tongue may become a frequent occurrence.
2. Bruxism: Teeth grinding or clenching can lead to accidental tongue bites.
3. Stress or anxiety: Nervousness or stress can cause people to inadvertently bite their tongue.
4. Inadequate denture fit: Ill-fitting dentures can cause irritation that may lead to tongue biting.
5. Habits: Certain habits such as nail-biting, lip-biting, or chewing on the inside of the cheek can cause the tongue to inadvertently get caught in the process.
6. Certain medications: Medications that contribute to dry mouth can increase the likelihood of biting the tongue.
7. Alcohol consumption: Drinking alcohol may cause a person to lose coordination, leading to increased chances of accidentally biting the tongue.
If tongue biting is occurring frequently, it is important to identify the cause and take appropriate steps to prevent it from occurring again. A visit to the dentist or doctor may help in identifying the root cause of the frequent tongue biting.
SYMPTOMS OF TONGUE BITE
Typically, the symptoms of tongue bite include:
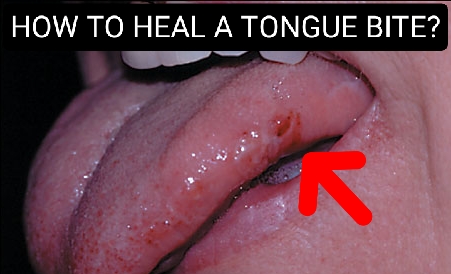
1. Pain or discomfort in the tongue area
2. Swelling or inflammation of the tongue
3. Redness or discoloration of the affected area
4. Difficulty in speaking or swallowing
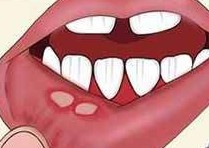
5. Bleeding or cuts in the tongue
6. Numbness or tingling sensation in the tongue
7. Formation of blisters or sores on the tongue
8. Fever or chills (in the case of an infection)
9. Bad breath or foul taste in the mouth
10. Difficulty in opening or closing the mouth.
HOW TO HEAL A TONGUE BITE?
Here are some ways to alleviate the pain of a tongue bite:
1. Rinse your mouth with warm salt water: Mix half a teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and rinse your mouth with it. Salt water will help to reduce swelling and inflammation.
2. Ice pack: Apply an ice pack to the affected area for 10-15 minutes. It will provide a numbing effect and reduce swelling.
3. Painkillers: Over-the-counter painkillers such as Tylenol, aspirin or ibuprofen can reduce pain and swelling.
4. Honey: Apply a small amount of honey to the affected area as it has anti-inflammatory properties that help to reduce pain and inflammation.
5. Aloe Vera: Aloe vera has natural cooling and soothing properties that can help with pain relief. Rinse your mouth with aloe vera juice or apply a small amount of aloe vera gel directly to the affected area.
If the pain does not subside after a few days, or if the tongue bite becomes infected, it is recommended to seek medical attention from a doctor or dentist.
IN SEVERE CASES
In severe cases where the tongue bite is very painful or does not heal, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Some severe cases may require medical treatment, such as:
1. Emergency medical attention: If the tongue bite is severe, it may require stitches or other medical care. Seek medical attention immediately if the tongue is bleeding heavily, there is severe pain or swelling, or if the bite appears to be infected.
2. Medication: In some cases, pain medication or antibiotics may be prescribed to help reduce pain and prevent infection.
3. Surgery: If the tongue is severely injured or the bite is deep, surgery may be necessary to repair the damage.
4. Dental treatment: If the tongue bite is caused by a dental issue such as a malocclusion or sharp edges on teeth, dental treatment may be necessary to prevent further tongue bites.
It is important to seek medical attention promptly if the tongue bite is severe or does not improve with home remedies.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, tongue biting can happen to anyone and can be caused by a variety of factors, including accidental biting during eating or talking, dental problems, sleep disorders, stress, anxiety, and seizures. Treatment depends on the severity of the tongue bite and can range from simple home remedies to medical intervention. In severe cases, it is important to seek medical attention to prevent infection and ensure proper healing. To prevent frequent tongue biting, it is recommended to maintain oral hygiene, address dental issues, manage stress and anxiety, and seek medical treatment for underlying conditions such as sleep disorders and seizures.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions regarding tongue biting:
1. How long does it take for a tongue bite to heal?
A: The healing time for a tongue bite depends on its severity. Minor tongue bites may heal within a few days, while more severe and deep bites may take several weeks to heal completely.
2. What should I do if I accidentally bite my tongue?
A: Rinse your mouth with warm salt water to prevent infection and reduce pain and swelling. Apply a cold compress to the affected area and avoid eating spicy, acidic, or crunchy foods. If the bite is severe or bleeding heavily, seek medical attention.
3. Can a tongue bite become infected?
A: Yes, if a tongue bite is not properly cleaned and cared for, it can become infected. Signs of infection include redness, swelling, pus, and fever. If you suspect an infection, seek medical attention immediately.
4. How can I prevent tongue biting?
A: To prevent tongue biting, avoid talking or eating too quickly and pay attention to your dental health. If you have sleep disorders, anxiety or seizures, seek medical treatment for these conditions.