Crossbite is a common dental condition that affects both children and adults. It occurs when the upper and lower teeth do not align properly and some of the upper teeth bite inside the lower teeth, while others bite outside the lower teeth when the jaws are closed. This misalignment can cause a wide range of issues, including difficulty with eating and speaking, jaw pain, and dental problems like tooth decay and gum disease. Fortunately, crossbite can be treated effectively with the right approach, whether that involves orthodontic treatment, surgery, or simple lifestyle changes. In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about crossbite, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
WHAT IS A CROSSBITE?
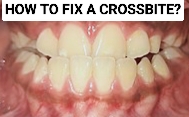
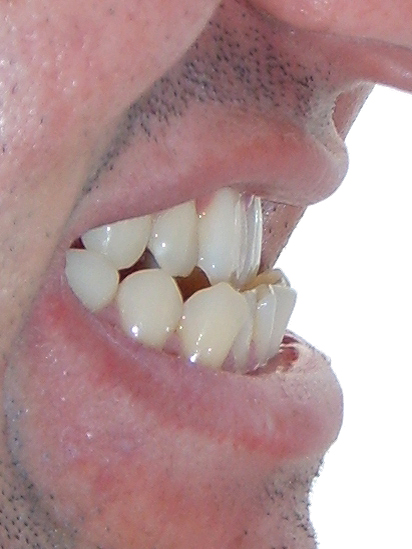
A crossbite is a dental condition where the upper teeth fall behind the lower teeth when biting down, instead of on top of them. It can occur on one or both sides of the mouth. Crossbites can cause issues with biting and chewing, speech impediments, and jaw pain. It is often corrected with orthodontic treatment.
Crossbite is a dental condition where the teeth of the upper and lower jaws do not align correctly. In a crossbite, some of the upper teeth bite inside the lower teeth, while others bite outside the lower teeth when the jaws are closed. This misalignment can cause problems with the teeth, gums, and jaw, and can lead to difficulty with eating and speaking.
SIGNS OF A CROSSBITE
If you suspect that you or someone you know may have a crossbite, an orthodontist or dentist can diagnose it through a physical examination and a series of diagnostic tests. However, there are a few signs that may indicate the presence of a crossbite:
1. Misaligned bite: A crossbite causes a misaligned bite where the upper or lower teeth are situated too far in or out compared to the other teeth.
2. Difficulty biting or chewing: A crossbite may make it difficult to bite or chew food properly
3. Jaw discomfort or pain: A crossbite can lead to jaw pain on one or both sides.
4. Speech difficulties: Crossbites can affect speech clarity, causing a lisp or other speech impediments.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is best to consult with an orthodontist or dentist to assess whether or not there is a crossbite. They can conduct a thorough examination and suggest an appropriate treatment plan if necessary.
DIAGNOSIS
There are several dental diagnostic procedures that can be used to diagnose crossbite, depending on the individual case. Here are a few examples:
1. Visual examination:
The dentist or orthodontist will visually examine the patient’s teeth and bite to look for signs of crossbite. They may also ask the patient about any symptoms they are experiencing.
2. Impressions or scans:
The dentist or orthodontist may take impressions or scans of the patient’s teeth to create a model of their bite. This model can help them to see the details of the bite and identify any issues such as a crossbite.
3. X-rays:
X-rays can be taken to get a better view of the internal structures of the teeth and jaw. This can help the dentist or orthodontist to see if there are any alignment issues that may be causing a crossbite.
4. Bite analysis:
The dentist or orthodontist may analyze the way the patient’s teeth come together when they bite down to determine if there is a crossbite present.
Ultimately, the best diagnostic procedure for crossbite will depend on the individual case and the preferences of the dentist or orthodontist.
TYPES OF CROSSBITE
There are two types of crossbites: anterior crossbite and posterior crossbite.
1. Anterior crossbite:
This occurs when the upper front teeth overlap the lower front teeth. Anterior crossbite can be caused by genetics, thumb sucking, or improper tooth development.

2. Posterior crossbite:
This occurs when the upper back teeth bite on the inside of the lower back teeth. Posterior crossbite can be caused by genetics, improper tooth development, or prolonged use of pacifiers.

Both types of crossbite can cause discomfort or pain when biting or chewing, jaw misalignment, and speech problems. It is important to seek treatment from a dental professional to correct a crossbite in order to avoid further complications.
PROBABLE CAUSES OF CROSSBITE
There can be several causes of crossbite, including:
1. Genetics: Crossbite can often be hereditary and may run in families.
2. Abnormal tooth development: If teeth do not develop properly, they can cause a misalignment of the teeth and jaws.
3. Mouth breathing: Chronic mouth breathing can cause the teeth and jaws to shift and lead to a crossbite.
4. Thumb sucking: Prolonged thumb sucking can cause the front teeth to move forward, leading to an anterior crossbite.
5. Prolonged use of pacifiers or bottles: Similar to thumb sucking, the prolonged use of pacifiers or bottles can cause the teeth to shift and lead to a crossbite.
6. Trauma: Injury to the jaw or teeth can cause a misalignment of the jaws and teeth, resulting in crossbite.
It is important to seek treatment for crossbite to avoid further complications and maintain good oral health.
EFFECTS OF CROSSBITE IF LEFT UNTREATED
If left untreated, crossbite can have several long-term effects on oral health and overall wellbeing, including:
1. Dental problems:
An uncorrected crossbite can lead to excessive wear on teeth, tooth decay, and gum disease, all of which can cause further dental problems.
2. Jaw pain:
Untreated crossbite can cause misalignment of the jaws, leading to temporomandibular joint (TMJ) pain, headaches, and neck pain.
3. Speech problems:
Crossbite can interfere with speech production, causing problems with pronunciation and articulation.
4. Eating difficulties:
Crossbite can affect a person’s ability to chew and bite properly, leading to eating difficulties and nutritional deficiencies.
5. Facial asymmetry:
Over time, an untreated crossbite can impact facial structure and lead to facial asymmetry.
In addition to these long-term effects, crossbite can also impact a person’s confidence and self-esteem due to cosmetic concerns with the appearance of their smile. Therefore, it is important to seek treatment for crossbite to prevent these complications and maintain good oral health.
HOW TO FIX A CROSSBITE?
The treatment of crossbite depends on the severity of the condition and your personal preferences. Following are the treatment options for crossbite:
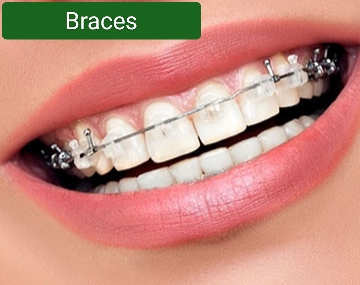
1. Braces or Clear Aligners:
Braces or clear aligners are the most common orthodontic treatment for crossbite. They work by gradually moving the teeth to the proper position.

2. Palatal Expansion:
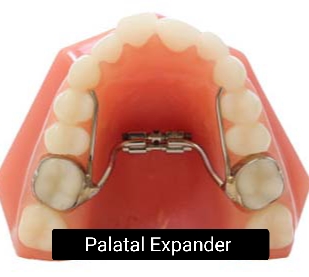
Palatal expansion is a procedure that widens the upper jaw to correct crossbite. This procedure is often recommended for children before their growth plates close.
3. Tooth extraction:
Sometimes, tooth extraction may be necessary to create space in the jaw to correct the crossbite.
4. Jaw Surgery:
Surgery may be needed in some severe cases of crossbite where the bones of the jaw need to be realigned to correct the bite.
5. Removable Appliances:
In some cases, your orthodontist may recommend using removable appliances like a bite plate or reverse headgear to correct your crossbite.
It’s important to remember that untreated crossbite can lead to several dental problems, so it’s essential to seek treatment from an orthodontist or dentist with experience in managing the condition.
CAN A CROSSBITE BE CORRECTED AT HOME?
It is not recommended to attempt to correct a crossbite at home. Crossbite is a dental condition that requires professional attention to properly diagnose and treat. Attempting to correct it at home without proper training and equipment can potentially worsen the condition or lead to other dental problems.
It’s best to consult with a qualified orthodontist or dentist who can provide you with the appropriate treatment options and develop an individualized treatment plan to correct your crossbite effectively. These professionals can also provide guidance on oral hygiene practices that can help maintain good oral health during treatment.
It is important to consult a dentist or orthodontist if you suspect that you or your child have crossbite, as prompt treatment can prevent potential complications down the line. With proper care, anyone with crossbite can enjoy improved oral health and a more confident smile.
FAQs
Q: What is a crossbite?
A: Crossbite is a dental condition where the upper and lower teeth do not align properly. In a crossbite, the teeth of the top and bottom jaw do not meet correctly when the jaws are closed, which can cause misalignment of the teeth, and jaw problems.
Q: What are the causes of crossbite?
A: Crossbite can be congenital meaning genetic. It can also be caused by bad habits like sucking a thumb or pacifier for an extended period, dental decay or loss of teeth, and jawbone abnormalities.
Q: What are the symptoms of a crossbite?
A: Symptoms of a crossbite may include uneven wear on teeth, difficulty eating or speaking, jaw pain and discomfort, and an uneven facial appearance. In some cases, patients may not experience any symptoms.
Q: How is a crossbite diagnosed?
A: An orthodontist can diagnose a crossbite through a comprehensive orthodontic evaluation, including a physical examination, X-rays, and other diagnostic tests.
Q: What are the treatment options for crossbite?
A: The treatment options for crossbite may include braces, custom-made orthodontic appliances, expanders, or extractions, depending on the severity or cause of the crossbite.
Q: How long does it take to correct a crossbite?
A: The duration of correcting a crossbite depends on the corresponding treatment modality, severity of the crossbite, and patient compliance.
Q: What are the consequences of not treating a crossbite?
A: Neglecting a crossbite can lead to several dental and emotional consequences, including tooth decay, gum disease, abnormal jaw growth, speech difficulties, facial asymmetry, and low self-esteem.
Q: Is crossbite treatable in adults?
A: Yes, crossbite is treatable in adults as long as there is no significant dental or medical contraindication. Orthodontic treatment options for adults may include braces, Invisalign aligners, or clear aligner therapy.