Dental extraction, also known as tooth extraction, is a dental procedure in which a tooth is removed from its socket in the jawbone.
Dental extraction is usually performed as a last resort when no other dental treatments can save a damaged or decayed tooth. In this article, we will examine everything you need to know about dental extraction, including why it is necessary, the different types of dental extractions, the risks and benefits, and the recovery process.
Why is Dental Extraction Necessary?
Dental extraction may be necessary for several reasons, including:
1. Damage to the Tooth: If a tooth is severely damaged or broken, it may not be possible to repair it with a filling, crown, or root canal treatment.
2. Tooth Decay: Tooth decay can cause cavities, which can become severe enough to require extraction.
3. Gum Disease: Gum disease is an infection that affects the gums and can cause the teeth to loosen and require extraction.
4. Overcrowding: When there is not enough space in the mouth for all the teeth to properly grow or line up, extraction may be necessary to improve the alignment of the teeth.
5. Orthodontic Treatment: In some cases, orthodontic treatment may require the extraction of one or more teeth to make room for the remaining teeth to shift into their proper position.
Types of Dental Extraction
There are two types of dental extraction:
1. Simple Extraction:
A simple extraction, is performed on a tooth that is visible and is easily accessible. The dentist first numbs the area around the tooth with a local anesthetic to minimize pain and discomfort. The dentist then uses a tool called an elevator to loosen the tooth and forceps to gently pull it out of the socket.
2. Surgical Extraction:
A surgical extraction, is required for teeth, that have not yet erupted ;or are broken off at the gumline, making them difficult to access. In some cases, a surgical extraction may also be necessary to remove a tooth, that is, impacted i.e. stuck in the jawbone). During a surgical extraction, the dentist makes a small incision in the gum tissue to access the tooth and then uses specialized instruments to remove the tooth.
COST OF DENTAL EXTRACTION
The cost of dental extraction varies depending on factors such as the location of the tooth, the complexity of the extraction, and the geographic location of the dental practice. On average, a simple extraction can cost between $75 to $300 per tooth, while a surgical extraction can cost between $225 to $600 per tooth.
If you have dental insurance, your plan may cover some or all of the cost of a dental extraction. It’s best to check with your dental insurance provider to understand your coverage before undergoing any dental procedures.
Additionally, many dental practices offer payment plans or financing options to help patients manage the cost of dental care. You can speak with your dentist’s office to see if they offer any such options.
PROCEDURE OF DENTAL EXTRACTION
The general procedure for dental extraction involves the following steps:
1. Local anesthetic is administered to numb the area surrounding the tooth to be extracted.
2. The dentist or oral surgeon will then use dental forceps to grasp the tooth and gently rock it back and forth until it loosens from the socket.
3. Once the tooth is loosened, the dentist or oral surgeon will use dental elevators to lift the tooth out of the socket.
4. Any remaining fragments of the tooth or roots may be carefully removed using a dental drill or forceps.
5. The extraction site is then cleaned, and the patient will be given instructions on how to care for the site to promote healing.
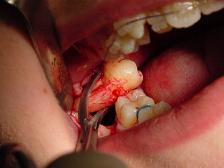
INSTRUMENTS USED
The following instruments may be used during the dental extraction procedure:

1. Local anesthetic syringe – Used to inject the anesthetic into the gum tissue around the tooth.
2. Dental forceps – Used to grasp and gently rock the tooth back and forth to loosen it from the socket.
3. Dental elevators – Used to lift the tooth out of the socket once it is loosened.
4. Dental drill – Used to remove any remaining fragments of the tooth or roots.
5. Surgical curette – Used to clean the extraction site after the tooth is removed.
It’s important to note that the specific instruments used may vary depending on the individual case and the preferences of the dentist or oral surgeon performing the procedure.

Risks of Dental Extraction
Dental extraction, like any dental or medical procedure, comes with risks and benefits. Some of the risks associated with dental extraction include:
1. Pain and Discomfort: You may experience pain and swelling in the extraction site following the procedure.
2. Bleeding: You may experience bleeding from the extraction site for several hours after the procedure.
3. Infection: There is a risk of developing an infection at the extraction site.
4. Nerve Damage: Nerve damage can occur during the extraction, leading to numbness or tingling in the lips, tongue, or chin.
Benefits Of Dental Extraction
1. Improved Dental Health: Removing a damaged or decayed tooth can prevent further damage to surrounding teeth and improve overall dental health.
2. Pain Relief: Extraction can relieve the pain and discomfort associated with a damaged or decayed tooth.
3. Better Appearance: Tooth extraction can improve the appearance of the teeth and smile.
Recovery Process
After dental extraction, it is essential to care for the extraction site properly to promote healing and prevent infection. Here are some tips on how to care for the extraction site:
1. Take Pain Medication: Your dentist may prescribe pain medication to help manage any pain or discomfort following the procedure.
2. Apply Ice: Applying ice to the cheek over the extraction site can help reduce swelling.
3. Avoid Rinsing or Spitting: Avoid rinsing or spitting for the first 24 hours following the procedure. It allows the blood clot to form at the extraction site.
4. Soft Diet: For the first few days following the procedure, it is best to stick to a soft diet. Avoid hard, crunchy, or chewy foods that may irritate the extraction site.
5. Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Continue brushing and flossing your teeth. But Avoid the extraction site for the first few days to prevent irritation.
Conclusion:
Dental extraction, is a common dental procedure that is necessary when a tooth is damaged, decayed, or causing crowding in the mouth. The procedure involves removing the tooth from its socket in the jawbone. While dental extraction comes with risks, such as pain and bleeding, it also has several benefits, including improved dental health and pain relief. Proper care of the extraction site is necessary for a full recovery, including taking pain medication, applying ice, sticking to a soft diet, and practicing good oral hygiene. If you have a damaged or decayed tooth, talk to your dentist about whether dental extraction is the right option for you.
FAQs
Q: Why do I need a dental extraction?
A: Dental extraction is necessary when a tooth cannot be saved due to extensive decay, periodontal disease, injury, or overcrowding.
Q: Is a dental extraction painful?
A: The area around the tooth will be numbed with local anesthesia, so you should not feel any pain during the procedure. However, you may experience some discomfort afterward, which can be managed with pain medication prescribed by your dentist.
Q: What should I expect after a dental extraction?
A: Following the extraction, you may experience some swelling and discomfort. Your dentist will provide specific instructions for aftercare, including how to manage any pain and how to care for the extraction site to promote healing.
Q: Are there any risks associated with dental extraction?
A: As with any procedure, there are some risks associated with dental extraction, such as bleeding, infection, or damage to adjacent teeth. These risks can be minimized by following your dentist’s instructions for aftercare.
Q: How long does it take to recover from a dental extraction?
A: Recovery time varies depending on the individual and the complexity of the extraction. Typically, the initial healing period lasts for about one to two weeks, during which time you should avoid strenuous exercise and consume a soft or liquid diet.
Q: Will I need a dental implant or bridge after a dental extraction?
A: Depending on the location of the extracted tooth, your dentist may recommend replacing it with a dental implant or bridge to prevent your teeth from shifting and to restore proper bite function.

