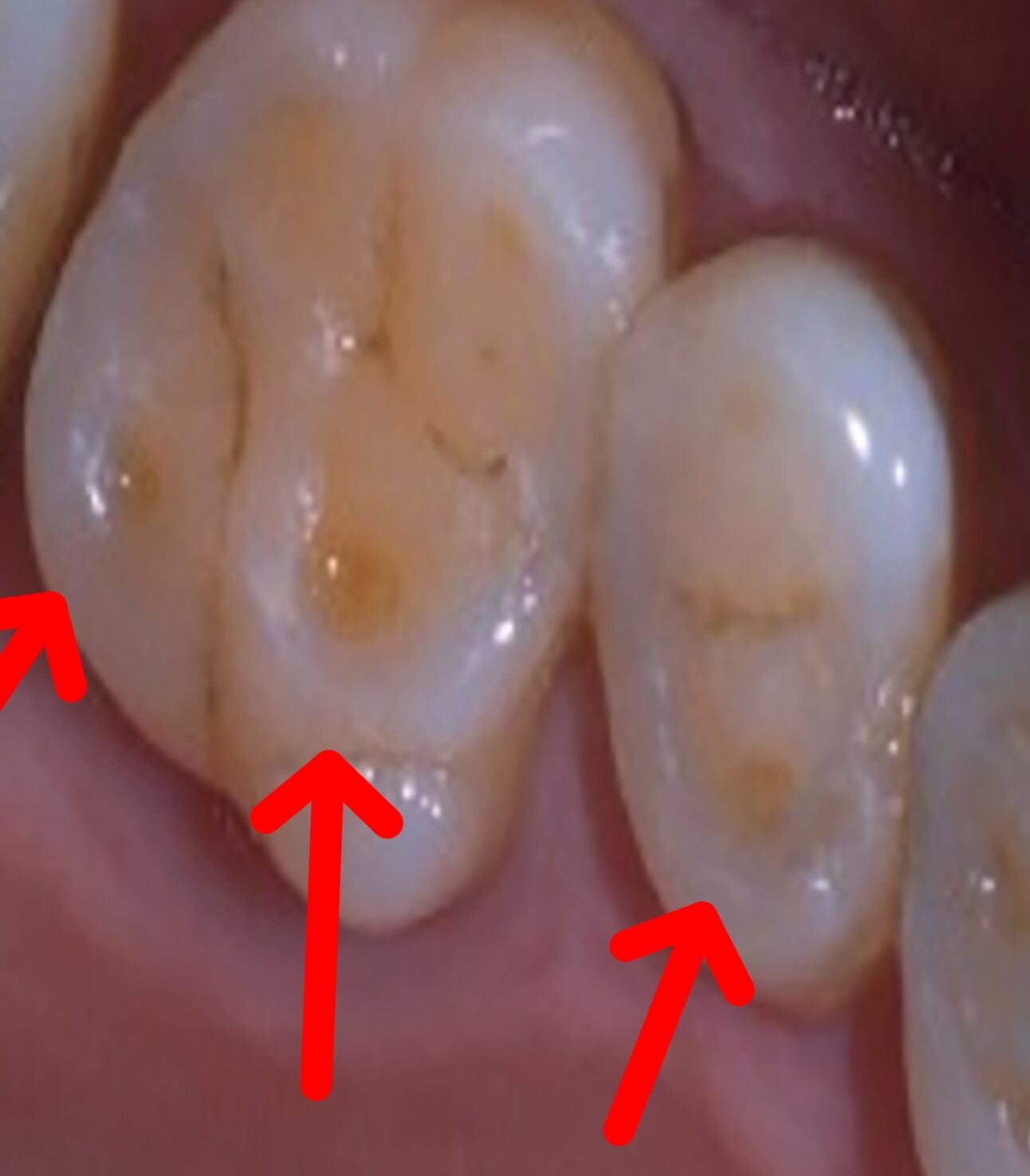
Tooth cupping, also known as dental cupping or dental erosion, refers to the loss of tooth enamel in a concave or cupped shape on the surface of the tooth. This condition is typically caused by the acidic erosion of tooth enamel over time. Tooth cupping can lead to tooth sensitivity, discoloration, and increased risk of cavities and tooth decay.
CAUSES OF TOOTH CUPPING
Tooth cupping, also known as dental erosion, can be caused by various factors, including:
1. Acidic foods and drinks: Consuming foods and drinks that are high in acid content, such as citrus fruits, soft drinks, sports drinks, and fruit juices, can cause erosion of the tooth enamel over time.
2. Gastrointestinal problems: Certain gastrointestinal conditions, such as acid reflux or frequent vomiting, can expose the teeth to stomach acid and cause erosion.
3. Dry mouth: A decrease in saliva production can lead to dry mouth, which can make it difficult for the mouth to neutralize acid and protect the teeth from erosion.
4. Teeth grinding: Grinding or clenching the teeth can cause the tooth enamel to wear down and increase the risk of erosion.
5. Over-zealous brushing: Brushing your teeth too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can cause the tooth enamel to wear away over time.
6. Medications: Certain medications, such as aspirin or antihistamines, can cause dry mouth and increase the risk of tooth erosion.
7. Genetic factors: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to tooth erosion, making them more susceptible to developing it.
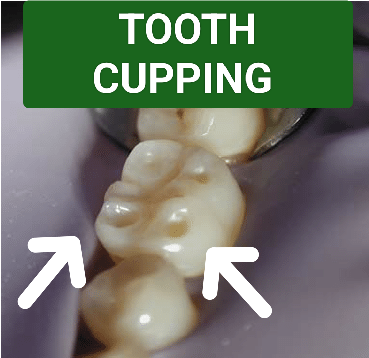
SYMPTOMS ASSOCIATED WITH TOOTH CUPPING
The signs and symptoms of tooth cupping or dental erosion may include:
1. Sensitivity: Tooth sensitivity is a common symptom of tooth cupping. You may experience discomfort or pain when consuming hot or cold foods and beverages.
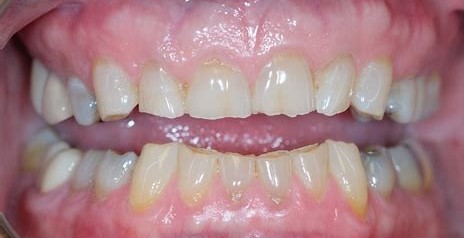
2. Discoloration: The affected teeth may appear yellowish or discolored.
3. Rough or uneven edges: Tooth cupping can cause the surfaces of your teeth to become rough or uneven.
4. Visible dents or pits: Eventually, tooth cupping can cause small dents, pits, or grooves on the surface of the teeth.
5. Transparent or thinning teeth: As tooth enamel erodes, the affected teeth may appear more transparent or thinner.
6. Chipping or cracking of teeth: Severely affected teeth may be prone to chipping or cracking, particularly along the edges.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, it is important to schedule an appointment with your dentist for a thorough examination and appropriate diagnosis. Early detection and treatment of tooth cupping can prevent further damage to your teeth.
PREVENTION
Tooth cupping, also known as dental erosion, can be prevented by following these measures:
1. Limit acidic foods and drinks: Avoid or limit consuming acidic foods and drinks such as citrus fruits, soft drinks, sports drinks, and fruit juices.
2. Use a straw for acidic drinks: Using a straw can help to limit the contact of acidic drinks with the teeth and reduce the risk of erosion.
3. Rinse after meals/snacks: Rinsing your mouth with water after meals and snacks can help to wash away food particles and neutralize the acid.
4. Chew sugar-free gum: Chewing sugar-free gum can stimulate saliva production, which can help to neutralize acids in the mouth.
5. Use a fluoride toothpaste: Fluoride toothpaste can help to strengthen the enamel and protect it from erosion.
6. Visit the dentist regularly: Regular dental check-ups can help to detect early signs of tooth erosion and prevent it from progressing.
7. Brush and floss properly: Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Flossing can help to remove food particles and prevent plaque buildup.

TREATMENT
The treatment for tooth cupping, also known as dental erosion, may depend on the severity of the condition. Here are some possible treatments:
1. Prescription fluoride:
The dentist may prescribe a fluoride gel or toothpaste to help restore the lost minerals and strengthen the tooth enamel.
2. Dental bonding:
For mild to moderate cases, dental bonding can be used to restore the lost tooth enamel. The dentist will apply a tooth-colored resin to the affected teeth and sculpt it to restore the original shape and size.
3. Veneers:
For more severe cases, porcelain or composite veneers can be used to cover the affected teeth and protect them from further erosion.
4. Crowns:
If the tooth erosion has caused significant damage to the tooth structure, a crown may be necessary to restore the tooth and protect it from further damage.
5. Lifestyle changes:
The dentist may recommend lifestyle changes, such as avoiding acidic foods and drinks and practicing good oral hygiene, to prevent further erosion.
In severe cases, a referral to a specialist may be necessary. It is important to seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent the erosion from progressing and causing more damage to the teeth.
RELATED ARTICLE- VENEERS VS LUMINEERS
ALSO READ – DENTAL CROWNS – (CAPPING) 101: AN AMAZING INSIGHT TO ALL YOUR QUERIES
FAQ’S FOR DENTAL CUPPING
Q: What is tooth cupping?
A: Tooth cupping, also known as dental cupping or dental erosion, is a condition where the enamel on the teeth wears away in a concave shape, forming cup-like indentations on the surface of the teeth.
Q: What causes tooth cupping?
A: Tooth cupping can be caused by a variety of factors, including acid erosion from acidic foods or drinks, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), alcohol consumption, certain medications, and tooth grinding or clenching.
Q: How can tooth cupping be prevented?
A: To prevent tooth cupping, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene, avoid acidic foods and drinks, limit alcohol consumption, and wear a mouthguard if you grind or clench your teeth.
Q: Can tooth cupping be reversed?
A: Unfortunately, once tooth enamel is worn away, it cannot be replaced. However, dental bonding or porcelain veneers can be used to cover the cupped areas and improve the appearance of the teeth.
Q: How is tooth cupping treated?
A: Treatment for tooth cupping depends on the severity of the damage. In some cases, tooth sensitivity can be treated with fluoride rinses or desensitizing toothpaste. If the damage is more severe, dental bonding or porcelain veneers may be necessary to cover the affected areas. In extreme cases, a dental crown may be needed.
Q: Is tooth cupping a serious condition?
A: While tooth cupping may not be a serious medical condition, it can lead to tooth sensitivity, cavities, and other dental problems if left untreated. It is important to address the underlying cause of tooth cupping and seek treatment if necessary.




Completely I share your opinion. I like this idea, I completely with you agree.