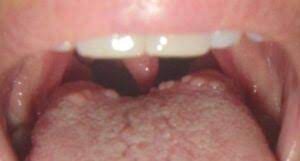
The answer to the question “why Do I Have Bumps on My Tongue?” , Let’s understand what are these bumps.
BUMPS ON THE TONGUE
The bumps on the back of the tongue are called Lingual Tonsils. They are clusters of lymphatic tissue, which are part of the body’s immune system and help in fighting off infections. The lingual tonsils are located at the base of the tongue and appear as small, rounded bumps or ridges on the surface of the tongue.
In most cases, the lingual tonsils are not visible or noticeable. They are usually only seen when they become enlarged due to an infection or inflammation, such as tonsillitis or pharyngitis. When they enlarge, they can cause discomfort, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, or even breathing problems.
If there are persistent bumps on the back of your tongue or other unusual changes to the tongue, it is important to seek medical attention from a doctor or dentist. They can help diagnose the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment.
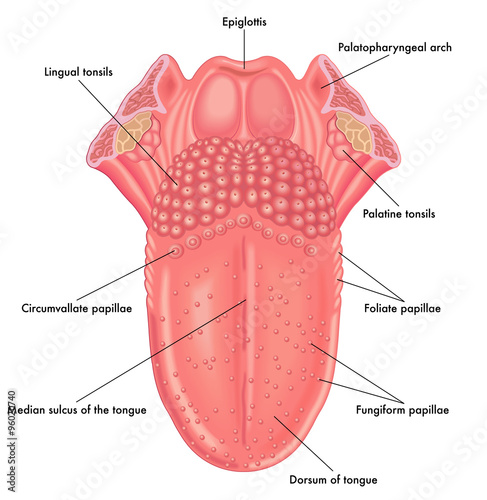
WHAT DO THE BUMPS ON TONGUE LOOK LIKE?
Bumps on the back of the tongue can vary in appearance depending on the cause. Here are some common types of bumps and their appearance:
1. Enlarged lingual tonsils:
These bumps are usually large and appear as raised, oval-shaped masses on the back of the tongue.
2. Canker sores:
These are small, round, or oval-shaped bumps with a yellow or white center and red borders. They can be painful and make speaking and eating difficult.
3. Oral thrush:
Oral thrush can cause white patches on the tongue, gums, or inside the cheeks. These patches may be slightly raised and can bleed when scraped.
4. Viral infections:
Bumps caused by viral infections can vary in appearance and may be accompanied by redness or inflammation.
5. Irritation from smoking or using tobacco:
Irritation from smoking or using tobacco products can cause small, white bumps or small red bumps on the back of the tongue.
It is important to consult a doctor or dentist for proper diagnosis and treatment if you have bumps on the back of the tongue that persist or worsen over time or that are accompanied by other symptoms.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF BUMPS ON TONGUE?
The causes of bumps on the back of the tongue can vary and may include:
1. Enlarged lingual tonsils – As mentioned earlier, the lingual tonsils are located at the base of the tongue and can become swollen or enlarged due to infections, inflammation or allergies.
2. Canker sores – These are small, painful ulcers that can develop on the tongue as well as on the lips, gums, and inside of the cheeks.
3. Oral thrush – This is a fungal infection caused by Candida fungus that can cause white patches or bumps on the tongue.
4. Viral infections – Certain viral infections such as the flu or common cold can also lead to bumps on the tongue.
5. Irritation from smoking or using tobacco products – This can cause bumps or ulcers on the tongue and other areas of the mouth.
6. Trauma or injury to the tongue – If the tongue is bitten, burned, or injured, bumps or ulcers can develop as a result.
Other less common causes of bumps on the back of the tongue can include
- Oral Cancer
- Oral Lichen Planus
- Sjogren’s syndrome, and
- Kawasaki disease.
If there are persistent bumps on the back of your tongue, it is important to consult a doctor or dentist to identify the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
SYMPTOMS ASSOCIATED WITH THE BUMPS ON THE BACK OF TONGUE
The symptoms of bumps on the back of the tongue can vary depending on the underlying cause. Some of the common symptoms associated with bumps on the back of the tongue may include:
1. Pain or discomfort: You may experience pain or discomfort while chewing, speaking or swallowing.
2. Swollen or enlarged bumps: The bumps on the back of the tongue may be swollen or appear to be larger than usual.
3. Sore throat: You may also experience a sore throat, which can be caused by inflammation or infection of the tonsils as well as the lingual tonsils on the back of the tongue.
4. Difficulty swallowing: Bumps on the back of the tongue can make it difficult to swallow food or even saliva.
5. Changes in taste: The presence of bumps on the back of the tongue can change your sense of taste.
6. White or yellow patches: In some cases, bumps on the back of the tongue can be accompanied by white or yellow patches on the tongue or throat.
7. Fever: Depending on the underlying cause, you may also have a fever along with other symptoms.
It is important to consult a doctor or dentist if you experience any of these symptoms or if you have bumps on the back of the tongue that do not go away or worsen over time.
TREATMENT
The treatment for bumps on the back of the tongue will depend on the underlying cause. Here are some possible treatments for common causes of bumps on the back of the tongue:
1. Enlarged lingual tonsils:
The treatment for enlarged lingual tonsils may include antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, or in severe cases, surgical removal of the tonsils.
2. Canker sores:
Canker sores usually heal on their own within a week or two. However, over-the-counter creams or gels, mouthwashes, and pain relievers may help relieve symptoms.
3. Oral thrush:
Oral thrush is treated with antifungal medications, either in the form of lozenges, tablets, or mouthwash.
4. Viral infections:
Viral infections are usually treated symptomatically with pain relief medications, rest, and hydration.
5. Irritation from smoking or using tobacco:
Avoiding smoking or using tobacco products can help relieve symptoms and prevent further irritation. Over-the-counter pain relievers, gels, and mouthwashes may also provide temporary relief.
If you have other underlying medical conditions causing bumps on the back of your tongue, your doctor may recommend further tests or additional treatments accordingly.
It is important to consult a doctor or dentist for proper diagnosis and treatment, especially if the bumps on the back of your tongue persist or worsen over time.
HOME REMEDIES FOR BUMPS ON TONGUE
While home remedies cannot replace professional medical advice, there are some remedies that may help alleviate the discomfort associated with bumps on the back of the tongue. Here are some home remedies you can try:
1. Saltwater rinse: Gargle with warm saltwater to reduce swelling, pain, and inflammation.
2. Aloe vera: Apply a small amount of aloe vera gel to the affected area to soothe irritation and promote healing.
3. Honey: Apply honey directly to the affected area to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
4. Ice or cold compress: Place a small ice cube or a cold compress on the affected area to reduce pain and swelling.
5. Turmeric: Mix turmeric powder with honey and apply the paste to the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain.
6. Chamomile tea: Gargle with chamomile tea to reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation.
7. Coconut oil: Apply a small amount of coconut oil directly to the affected area to soothe pain and irritation.
It is important to note that these home remedies are not a substitute for medical treatment. If your symptoms persist or worsen despite trying home remedies, consult a doctor or dentist for proper evaluation and treatment.
The answer to the question “why Do I Have Bumps on My Tongue?” , Let’s understand what are these bumps.
BUMPS ON THE TONGUE
The bumps on the back of the tongue are called Lingual Tonsils. They are clusters of lymphatic tissue, which are part of the body’s immune system and help in fighting off infections. The lingual tonsils are located at the base of the tongue and appear as small, rounded bumps or ridges on the surface of the tongue.
In most cases, the lingual tonsils are not visible or noticeable. They are usually only seen when they become enlarged due to an infection or inflammation, such as tonsillitis or pharyngitis. When they enlarge, they can cause discomfort, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, or even breathing problems.
If there are persistent bumps on the back of your tongue or other unusual changes to the tongue, it is important to seek medical attention from a doctor or dentist. They can help diagnose the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment.

WHAT DO THE BUMPS ON TONGUE LOOK LIKE?
Bumps on the back of the tongue can vary in appearance depending on the cause. Here are some common types of bumps and their appearance:
1. Enlarged lingual tonsils:
These bumps are usually large and appear as raised, oval-shaped masses on the back of the tongue.
2. Canker sores:
These are small, round, or oval-shaped bumps with a yellow or white center and red borders. They can be painful and make speaking and eating difficult.
3. Oral thrush:
Oral thrush can cause white patches on the tongue, gums, or inside the cheeks. These patches may be slightly raised and can bleed when scraped.
4. Viral infections:
Bumps caused by viral infections can vary in appearance and may be accompanied by redness or inflammation.
5. Irritation from smoking or using tobacco:
Irritation from smoking or using tobacco products can cause small, white bumps or small red bumps on the back of the tongue.
It is important to consult a doctor or dentist for proper diagnosis and treatment if you have bumps on the back of the tongue that persist or worsen over time or that are accompanied by other symptoms.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF BUMPS ON TONGUE?
The causes of bumps on the back of the tongue can vary and may include:
1. Enlarged lingual tonsils – As mentioned earlier, the lingual tonsils are located at the base of the tongue and can become swollen or enlarged due to infections, inflammation or allergies.
2. Canker sores – These are small, painful ulcers that can develop on the tongue as well as on the lips, gums, and inside of the cheeks.
3. Oral thrush – This is a fungal infection caused by Candida fungus that can cause white patches or bumps on the tongue.
4. Viral infections – Certain viral infections such as the flu or common cold can also lead to bumps on the tongue.
5. Irritation from smoking or using tobacco products – This can cause bumps or ulcers on the tongue and other areas of the mouth.
6. Trauma or injury to the tongue – If the tongue is bitten, burned, or injured, bumps or ulcers can develop as a result.
Other less common causes of bumps on the back of the tongue can include
- Oral Cancer
- Oral Lichen Planus
- Sjogren’s syndrome, and
- Kawasaki disease.
If there are persistent bumps on the back of your tongue, it is important to consult a doctor or dentist to identify the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
SYMPTOMS ASSOCIATED WITH THE BUMPS ON THE BACK OF TONGUE
The symptoms of bumps on the back of the tongue can vary depending on the underlying cause. Some of the common symptoms associated with bumps on the back of the tongue may include:
1. Pain or discomfort: You may experience pain or discomfort while chewing, speaking or swallowing.
2. Swollen or enlarged bumps: The bumps on the back of the tongue may be swollen or appear to be larger than usual.
3. Sore throat: You may also experience a sore throat, which can be caused by inflammation or infection of the tonsils as well as the lingual tonsils on the back of the tongue.
4. Difficulty swallowing: Bumps on the back of the tongue can make it difficult to swallow food or even saliva.
5. Changes in taste: The presence of bumps on the back of the tongue can change your sense of taste.
6. White or yellow patches: In some cases, bumps on the back of the tongue can be accompanied by white or yellow patches on the tongue or throat.
7. Fever: Depending on the underlying cause, you may also have a fever along with other symptoms.
It is important to consult a doctor or dentist if you experience any of these symptoms or if you have bumps on the back of the tongue that do not go away or worsen over time.
TREATMENT
The treatment for bumps on the back of the tongue will depend on the underlying cause. Here are some possible treatments for common causes of bumps on the back of the tongue:
1. Enlarged lingual tonsils:
The treatment for enlarged lingual tonsils may include antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, or in severe cases, surgical removal of the tonsils.
2. Canker sores:
Canker sores usually heal on their own within a week or two. However, over-the-counter creams or gels, mouthwashes, and pain relievers may help relieve symptoms.
3. Oral thrush:
Oral thrush is treated with antifungal medications, either in the form of lozenges, tablets, or mouthwash.
4. Viral infections:
Viral infections are usually treated symptomatically with pain relief medications, rest, and hydration.
5. Irritation from smoking or using tobacco:
Avoiding smoking or using tobacco products can help relieve symptoms and prevent further irritation. Over-the-counter pain relievers, gels, and mouthwashes may also provide temporary relief.
If you have other underlying medical conditions causing bumps on the back of your tongue, your doctor may recommend further tests or additional treatments accordingly.
It is important to consult a doctor or dentist for proper diagnosis and treatment, especially if the bumps on the back of your tongue persist or worsen over time.
HOME REMEDIES FOR BUMPS ON TONGUE
While home remedies cannot replace professional medical advice, there are some remedies that may help alleviate the discomfort associated with bumps on the back of the tongue. Here are some home remedies you can try:
1. Saltwater rinse: Gargle with warm saltwater to reduce swelling, pain, and inflammation.
2. Aloe vera: Apply a small amount of aloe vera gel to the affected area to soothe irritation and promote healing.
3. Honey: Apply honey directly to the affected area to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
4. Ice or cold compress: Place a small ice cube or a cold compress on the affected area to reduce pain and swelling.
5. Turmeric: Mix turmeric powder with honey and apply the paste to the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain.
6. Chamomile tea: Gargle with chamomile tea to reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation.
7. Coconut oil: Apply a small amount of coconut oil directly to the affected area to soothe pain and irritation.
It is important to note that these home remedies are not a substitute for medical treatment. If your symptoms persist or worsen despite trying home remedies, consult a doctor or dentist for proper evaluation and treatment.